What is Immersive Technology? Definition and Insights
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- What is an Immersive Experience?
- What Types of Immersive Experiences Are There?
- What is Immersive Technology?
- How are Immersive Experiences Built?
- How Do You Define the Level of Immersion?
- Where are Immersive Experiences Used?
- Why do Businesses Prefer Immersive Experiences?
- How to Assess the Quality of an Immersive Experience?
- Immersive Experiences Examples and Use Cases
- MEDICAL VR INTUBATION SIMULATION
- AEROSPACE VR MAINTENANCE SIMULATION
- INSTRUMENTATION LABORATORY HEMOCELL IN VR
- Immersive Experiences in The Metaverse
- Conclusion
- FAQ
- How Much Does it Cost to Build a VR Experience?
Author: Alex Dzyuba, Lucid Reality Labs Founder & CEO
Table of Contents
- What is an Immersive Experience?
- What Types of Immersive Experiences are There?
- What is Immersive Technology?
- How are Immersive Experiences Built?
- How Do You Define the Level of Immersion?
- Where are Immersive Experiences Used?
- Why Do Businesses Prefer Immersive Experiences?
- How to Assess the Quality of an Immersive Experience?
- Immersive Experiences Examples and use Cases
- Immersive Experiences in the Metaverse
- Conclusion
- FAQ
It’s always essential to go to the roots to understand and fully grasp the concept. Here, many questions may arise, including “What is immersive,” “What does immersive mean,” “What is the definition of immersive,” or “How to define immersive.” Thus, let’s first talk about the word “immersive” itself. Research conducted by the Bang & Olufsen research group in cooperation with Aarhus University and Technical University of Denmark authors defines immersive as a “state of deep mental involvement in which the subject may experience disassociation from the awareness of the physical world due to a shift in their attentional state.”
Immersive definition or immersive meaning includes activities capable of simultaneously engaging, entertaining, involving, and captivating us. From the technological perspective, the word immersive describes an experience, activity, or environment that can include users to the extent that they feel physically present and engaged in real life. Sometimes, cognitive concepts are used to describe immersion, such as transportation, flow, and, most frequently, presence. However, immersion is often more associated with the XR technical aspects than simply the sense of presence itself.
What is an Immersive Experience?
Today, one can hear the expression “immersive experience” about practically any topic or industry, from Healthcare, Education, and Manufacturing to Art, Gaming, and Entertainment. It is one of these terms, like the Metaverse, we all understand but often need help to define and explain without turning to particular examples. Thus, we decided to dedicate an article to uncovering the topic, determining immersive experiences, and discussing how they are built and the technology behind them. We will cover the questions of immersive experience meaning, what makes an experience immersive, what immersive experiences are like, look at some actual cases, and talk about the role immersive experiences will play in the Metaverse.
If we were to ask ourselves what is an immersive experience or how to define immersive experience. The answer would be — an immersive experience is an artificially created fully digital or digitally enhanced setting where users can feel a sense of sensory presence facilitated through immersive technology, such as Extended Reality (XR). It is important to note that XR is an umbrella term for Augmented, Virtual, and Mixed Reality technologies. The immersive technology capabilities allow to submerge and give a sense of realism to an environment, interaction, or setting as if it were happening in real life. So, at the end of the day, what is an immersive experience? An immersive experience is a full or partial digital surrounding that involves the user’s multiple sensory modalities, including visual, sound, motion, pressure, and even smell.
What Types of Immersive Experiences Are There?
There are several types of immersive experiences. They all differ by technical capabilities, level of submersion, and degree of digital enhancement. Immersive experiences include Augmented, Virtual, and Mixed Reality, each with unique purposes and capabilities. Augmented Reality enhances the real world with digital twins and visual overlays. Virtual Reality allows users to submerge into a virtual dimension, which can be built as a digital twin of the real-life counterpart, where they can interact remotely within the artificially created world and with other users. Mixed Reality combines the capabilities of AR to overlay real objects with the VR-created interactable digital world, enhanced by the digital twin technology. All three types can be used for various activities, from immersive interaction and gaming to immersive learning, training, and education.
The digital twin approach allows the creation of 1-to-1 digital replicas of any environment, function, item, response, or person, making it possible to build truly immersive experiences that instantly engage users. The growing advancement of software technology provided the tools to develop digital twins with unprecedented visual fidelity, looking and feeling like their real-life counterparts.
What is Immersive Technology?
So, what is an actual immersive technology definition? Is there an outlined immersive technology meaning? Immersive experience technology is how the immersive experience is achieved. The global immersive technology market is expected to land at USD 134.18 billion by 2030 and includes software and hardware components. The following rational questions would be — what is immersive technology, and how does immersive technology work? In the immersive experience, the hardware acts as a means or medium. Software is used to create an immersive setting and environment that allows users to feel present and engaged.
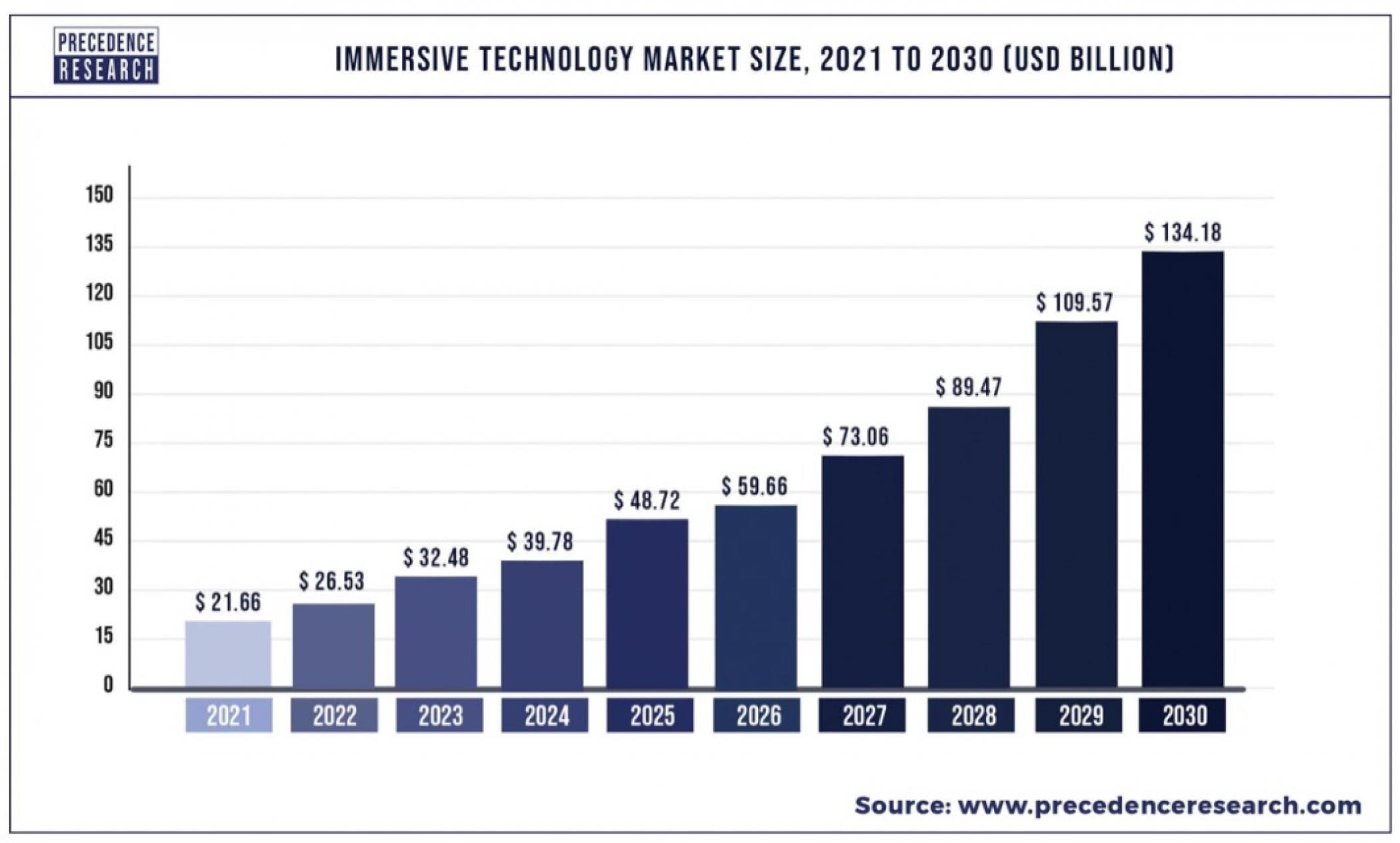
Immersive technology market size
When speaking of hardware, one can refer to mostly head-worn types of immersive technology
devices, like glasses and headsets that have full or partial XR capabilities. Meta Oculus, Microsoft Hololens, Varjo, Magic Leap, Pico Neo, and the HTC VIVE series are examples of immersive technology from the most well-known XR devices and immersive mixed reality technology. The software fraction of the immersive technology includes programs and platforms, tools, and approaches that allow developers to 3D model and create environments, surroundings, characters, animation, and much more. These parts must work in unison to make the artificially created digital elements or even entire worlds feel and look like they were part of real life.
As we have become acquainted with the definition of immersive technologies description, immersive technologies, and immersive technology types, we can already start wondering about and imagining potential implementation. Quite a few possible business ideas could come to mind. But before we get to explore concepts like “How does immersive technology improve work performance?”, “how does immersive technology improve work conditions?” or even “How does immersive technology improve work culture?” let’s discover how immersive experiences are built.

Image source: Meta (Meta quest pro)
How are Immersive Experiences Built?
There are several pillars an immersive experience is built on, including UX, Engineering, and Art. A comprehensive team of specialists is usually involved in the development process, from Project Managers and Analysts to 3D artists, Software Engineers, and QAs, responsible for their respective parts in the development. Depending on the project, the development process can start with the Discovery Phase or the Pre-Development, followed by the Development Phase, Support Phase, and Post-Development Phase. They are all aimed at the iterative and incremental development of a fully operational immersive experience ready for the end-user. But how does immersive technology work, or more like, how do you define the immersion itself?
How Do You Define the Level of Immersion?
There are many different visions and concepts of the level, degree, state, or immersion type. Some identify only physical and mental immersion, while others identify systems, spatial, empathic/social, and narrative/sequential immersions. Some studies suggest defining the level of immersion based on five criteria based on the user’s perception – the Surrounding, the Inclusivity, the Extensiveness, the Matching, and the Vividness. Surrounding is the Field of View (FoV) inside the environment, while Inclusivity defines the level at which external distractions like sound or controllers impact the level of environment believability. Extensiveness is the number of stimulus modalities affected by a stimulus, such as light, sound, taste, temperature, pressure, and smell. Matching is the extent to which the user’s movements reflect what they see inside the experience. Vividness is the level of visual fidelity and quality of the optic resolution. Other studies describe two perspectives – the objective property of a technology or system that can be measured and quantified. And the individual’s psychological state of the user’s attention being caught and adsorbed by the immersive experience.
Thus, the level of immersion can be defined as the combination of two factors – the degree of physical or sensory absorption and the state of psychological involvement with the developed immersive experience.
Where are Immersive Experiences Used?
There are countless possibilities to use immersive experiences for business and recreational activities. On the one hand, one can use them for art, music, entertainment, gaming, and recreational purposes. On the other hand, businesses and institutions can use immersive experiences to enhance education, training, risk and safety management, manufacturing, planning, and assessment. There are already many cases of immersive experience implementations in Healthcare, Pharma, MedTech, Education, Manufacturing, and other vastly growing industries. And will be even more immersive digital experiences. Immersive experiences already allow specialists to feel present in an artificially created environment.
Why do Businesses Prefer Immersive Experiences?
Businesses have been investing more in immersive technology over the past year, primarily due to the technological advancement, growing level of fidelity, and capabilities of immersive experiences. They allow for optimizing costs, including logistics and training, opportunities to develop a sense of accomplishment, train and operate in a risk-free environment, practice, make mistakes, learn, and improve. Immersive experiences can enhance products, processes, activities, and social interactions. With more industries and businesses bringing AR, VR, and MR to their everyday work environments, we are bound to see these technologies integrated into our daily lives more seamlessly in the foreseeable future.
How to Assess the Quality of an Immersive Experience?
Assessing the actual quality of an immersive experience can be challenging as there are no fundamental defined standards and still existing knowledge gaps in understanding the concept of immersion. Today, the assessment is primarily done by the end-user, meaning that the evaluation can sometimes be reasonably biased and subjective due to the difference in personal perception. As with many other assessments, individual users often use the Mean Opinion Score (MOS) or Questionnaire format. Which allows evaluating the experience quality respectively quantitatively or qualitatively. However, it still can give a reasonably vague idea, as each user judges the importance of each assessment point. For some, the UI/UX would play the most critical role; for others, the level of engagement would be essential. Some users consider the level of comfort as fundamental. The end users are the ones who define the quality of the immersive experience, as they are the ones who engage and interact with it. It is always essential to identify key evaluation metrics, as well as collect and evaluate individual feedback to have a comprehensive understanding of the immersive experience quality.
Immersive Experiences Examples and Use Cases
Every year, more immersive experiences are being developed for business and consumer use, each serving its purpose. Following, we would like to showcase some immersion experience examples from the Healthcare, MedTech, and Aerospace industries. While there are many more immersive technologies examples, these three cover a broad scope of implementation and functionality. These immersive technology examples include the use of Oculus Quest hardware.
MEDICAL VR INTUBATION SIMULATION
Medtronic McGRATH™ MAC VR Intubation Simulation is an interactive and immersive VR intubation simulation experience created with Medtronic to demonstrate the product and to train practitioners and medical students. It presents the usage of the McGRATH™ MAC video laryngoscope as the standard of care by educating participants on how to perform an intubation procedure with various patients and the complexity of intubation scenarios. The immersive simulation provides an excellent opportunity for medical specialists and students to enhance their skills and get new experiences in a realistic and fun way. It also offers the chance to train remotely and safely with maximum impact. Find out more.
AEROSPACE VR MAINTENANCE SIMULATION
The main objective of the project was to create a VR for jet turbine engine maintenance training environment for specialists in charge of regular technical reviews and checks of civil aircraft, including every step of the procedure from disassembling to cleaning, oiling, testing, and reassembling, to improve the quality of performed maintenance work. The simulation enables users to train and ensure process precision, reduce the number of corrective steps required, minimize engine post-maintenance release time, and process lead time. Find out more.
INSTRUMENTATION LABORATORY HEMOCELL IN VR
The project’s objective was to create a VR environment constructor where the client could create 1-to-1 virtual visualizations of the future laboratory according to their customer’s requirements. The virtual space would allow customers to visit and observe the future laboratory with pre-installed equipment. Find out more.
Werfen | Instrumentation Laboratory HemoCell in VR
Immersive Experiences in The Metaverse
Gartner predicts that 40% of major global organizations will rely on technology capabilities like digital twin, spatial computing, and Web 3.0, the Metaverse. The Metaverse has been a significant buzzword since 2021, growing its recognition and stirring global discussions for quite some time now. Many of these discussions run in parallel with the topic of immersive experiences, as they will be one of the comprehensive technology pillars that will provide a certain level of immersion in the Metaverse. As the concept of the Metaverse may seem confusing for some, here is how Alex Dzyuba, the Lucid Reality Labs CEO, defines the Metaverse.
ALEX DZYUBA, LUCID REALITY LABS CEO“The concept will blend our physical and digital existence, an open and expansive universe that will transition users from flat 2D environments into immersive and interactive 3D. The Metaverse is a common, ungoverned, and, most importantly, co-created existence. It consists of many Metaverse worlds with open standards and no physical borders. We are talking about a decentralized, scalable, and autonomous iteration that allows users to connect into a unified existence from any device. Ideally, an immersive, interactable, smart, intuitive, and digitally enhanced environment which could be both artificially created or real-time augmented, enhanced by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML).”
Today, immersive experiences in the context of the Metaverse refer to experiences that allow us to interact remotely and collaborate. Even though the concept of Metaverse was made relatively famous by Mark Zuckerberg, can we imagine Meta VR technology is critical to immersion for users globally? Probably not; however, Meta could become one primary technology key to Metaverse gaming immersion, capable of making videos immersive Metaverse push.
But speaking of the future, the immersive experiences in the Metaverse will advance much further, enabling users to submerge into connected virtual worlds, feeling present as an extension of their real-life existence, capable of more than making videos immersive Metaverse. In the long run, we envision immersive experiences in the Metaverse that allow users to engage in various activities and define how to experience the Metaverse. These activities can be anything from working in a connected virtual workspace or attending an educational institution to having routine hospital check-ups or specialist consultations while remaining remote, present, and connected simultaneously. With all said, there are still quite a few challenges that will require solving to advance in this direction.
Conclusion
Immersive experiences are becoming truly remarkable tools already used in numerous industries. With the development of XR headsets and digital twin technology, visual fidelity will soon reach the next generation of realism, bringing a sense of unprecedented immersion that will enhance the digital presence of businesses and users worldwide. As the technology develops, it will bring countless new possibilities in the Metaverse and Web 3.0, improving real-life interactions and providing limitless new real-time digital opportunities.
FAQ
How Much Does it Cost to Build a VR Experience?
Several factors can impact the Virtual Reality development cost, including but not limited to the technology stack, complexity of experience, project timeframe, desired hardware, and many more. For some projects, starting with the Discovery Phase is best to minimize risks and optimize costs, allowing for planning the project so that success is predictable.
